It took two planes, a road trip, and a rickety speedboat to transport me to the Kurdistan Region of Iraq in January 2003. It was then the run-up to the U.S.-led invasion, and journalists were competing to enter, with neighboring Iran, Turkey and Syria not making things easy.
After a six-day wait in Damascus, I boarded a wobbly charter plane and flew to the border town of Qamishli. The journey continued by car, past oil rigs and into Malakia, where I took a speedboat ride across the Tigris River. On the other side, a large sign, “Welcome to Kurdistan,” greeted new arrivals stepping onto the shore. It was the unofficial border crossing at Faysh Khabur – or peshkapur in Kurdish. Then by road I traveled to a regional political bureau in Zakho to register my arrival, and from there it was onward to Erbil.
I was among a few journalists who had managed to enter the country as the war approached. It wasn’t Baghdad, but it was a part of Iraq about which little news was being reported in the mainstream media, especially after the No-Fly Zone had been imposed following Saddam Hussein’s defeat in the 1991 Gulf War. The zone had permitted the establishment of the autonomous Kurdish Regional Government (KRG), but it had also left the cities under its jurisdiction walled in and isolated from the world. My assignment was to gauge the mood among the Kurds in the run-up to the invasion.
“Nobody knows much about the Kurds,” my editor had told me flippantly. “Let’s humanize them. Find out what they eat, whether they go to the cinema, what they think of the upcoming U.S. invasion,” he instructed.
I spoke to a cross section of Kurds, including shopkeepers in the bazaars, truck drivers, communists, former political prisoners, survivors of the 1988 Halabja chemical attack, peshmerga commanders, and civil society activists. The optimism was unanimous. The U.S. must invade, and Saddam Hussein must go, along with the crippling sanctions that had so cruelly impeded progress in the semi-autonomous Kurdish region. For the Kurds, the war represented hope for a temptingly better future.

Erbil, also called “Hawler” by the Kurds, is an ancient city with an estimated population of around 1,600,000. It had always been an important regional trade center, with roads to Turkey, Iran, and Syria. The famous Hamilton Road constructed under British rule in 1928-32 by Archibald M. Hamilton runs from Erbil through the mountains to the Iranian border.
I stayed at the Chwar Chra Hotel, which at the time was the hotel of choice for most foreign journalists, politicians, and aid workers. It provided good security, clean rooms, and fewer power cuts than elsewhere. Under Iraqi rule after World War I and during the Kurdish struggle against Saddam in the 1970s, Erbil’s infrastructure had largely been neglected. Even after the establishment of the KRG, Erbil continued to suffer economically due to the economic blockade imposed upon it by Saddam and to the UN sanctions against Iraq.
The Chwar Chra boasted a restaurant that served succulent local dishes but was also a meeting place for the Who’s Who of Erbil. More importantly, the name of the establishment commemorated the short-lived ‘Mahabad’ Republic in Iranian Kurdistan, a tragic chapter of Kurdish history that offered foreigners a first glimpse into the Kurdish psyche. While Kurds looked to the future with hope, they would never forget the past.
In 1945, with backing from the Soviet Union, Kurdish politician and jurist Qazi Muhammed had founded the first ever independent Kurdish state in the city of Mahabad in Iran. Mustafa Barzani was appointed Minister of Defense and commander of the republic’s army. When Iranian forces engaged the forces of the Republic of Mahabad, Barzani quickly proved his reputation, as his forces inflicted defeats on the Iranian divisions and were one of the few who did not surrender or defect to the advancing Iranian forces.
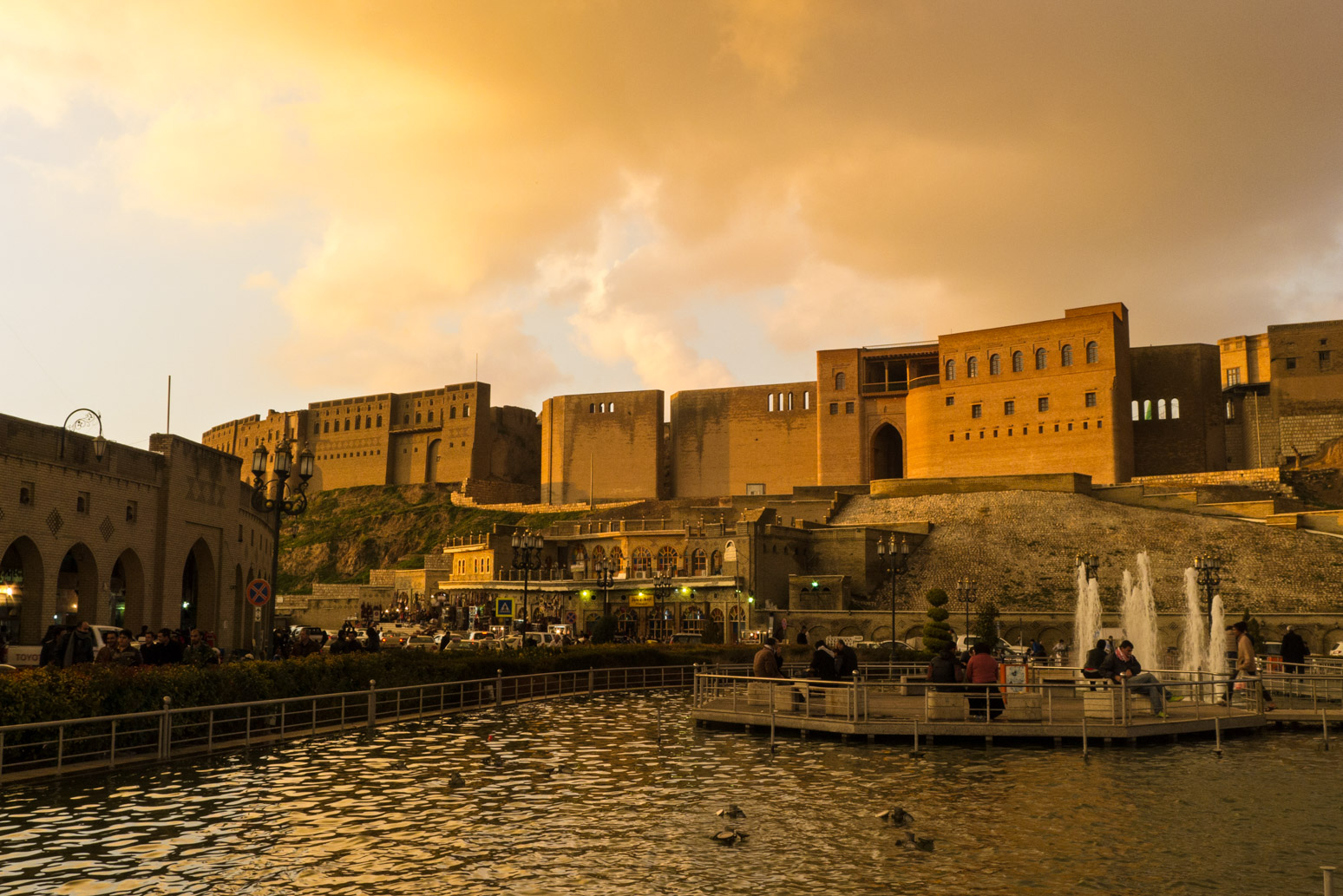

However, less than a year later, in December 1946, Iranian forces invaded the city and hanged Qazi Muhammed and his colleagues in the now iconic Chwar Chra square. Barzani and his followers managed to evade capture by finding refuge first in Armenia, later in Azerbaijan. After spending periods of time across the Soviet Union, he returned to Iraq and engaged in numerous insurgencies against Baghdad.
At the time of my first visit to Erbil in January 2003, Barzani’s son Massoud was heading the Kurdistan Democratic Party that he had co-founded with Qazi Muhammed. I interviewed him then.
“We are not thinking of participating in the war because we are focusing on the day after the regime changes,” he told me. “For several reasons, it would be very difficult for us to take part in this war. We don't intend to move our troops outside of Kurdish-ruled areas, and within this region, there are no targets for us to hit.”
By the time of my second visit to Erbil in the winter of 2005, Massoud Barzani had been elected as the President of the Kurdistan Region and it was, as he put it, “the day after the regime change.” Saddam was gone, the Baath party was destroyed, and it was finally time to build. Fortunes flowed into the Kurdish region, mostly from the Gulf countries and Turkey. Kurdish-administered northern Iraq was a blank slate, and risk-taking entrepreneurs from around the world were parachuting in. Soon, there would be two new airports, several new housing projects, shopping malls, five-star hotels, and Western fast-food chains.
Today, the presidency of the Kurdistan Region is held by Mustafa’s grandson, Nechirvan Barzani, while Massoud’s son Masrour Barzani is Prime Minister. In a nod to cross-Kurdish alliance, Qubad Talabani from neighboring Sulimaniyah is Deputy Prime Minister.
Traveling to Erbil no longer entails crossing the Tigris by speedboat or long car drives, as Erbil International Airport is now on par with global standards, with a VIP lounge offering croissants, cappuccinos, and Levantine treats like manakish and lahmajoon.
With much of the construction nearly complete, Erbil now boasts a skyline fit for any self-respecting Gulf country. High-end housing complexes, sushi bars, franchise fast-food restaurants such as Hardee’s and KFC, and other shops are found throughout the city, as are international hotel chains such as Rotana and Divan (Marriott and Hilton are set to open in the near future as well). The favorite spots of European expats include a German beer garden and a restaurant in the hip section of Ainkawa.
But though Erbil residents look back with pride on their recent days of struggle and triumph, there is far more history in Erbil dating to the fifth millennium BC. At the heart of the city lies the ancient Citadel of Erbil and the Mudhafaria Minaret. The earliest historical reference to the region dates to the Third Dynasty of Ur of Sumer, when King Shulgi mentioned the city of Urbilum. Over the millennia, Erbil has been ruled by such empires as the Sumerians, Assyrians, Babylonians, Medians, and Achaemenids and then later by the Sassanid Persians, Greeks, Parthians, Arabs, and Ottomans. In fact, Erbil was already an ancient city when in 331 BCE Alexander the Great defeated the Persian king Darius III at the Battle of Gaugamela, also known as the Battle of Arbela (Erbil) in 331 BCE, ending the Achaemenid Empire and leading to the downfall of Darius.

Visitors to Erbil’s archeological museum will find a large collection of pre-Islamic artefacts, particularly the art of Mesopotamia. The city is also a center for archaeological projects in the area and was designated as Arab Tourism Capital 2014 by the Arab Council of Tourism. In July 2014, the Citadel of Erbil was inscribed as a World Heritage Site.
As cities go, Erbil is a wonderful mélange of the old and the new. Thousands of years going back to the fifth millennium BC, through the pre-Islamic era, and up to modern times reveals today's Erbil as a city that does not bury its heritage but proudly displays it instead. It is rich with history, replete with opportunity, and ready to compete with other first-rate cities around the region.
Tanya Goudsouzian is a journalist, author and editor specializing in Afghanistan and Iraq affairs. She has reported for various international media outlets, including Al Jazeera English, RFE/RL and Le Monde Diplomatique. She is recognized for interviews with leading political figures including presidents of Iraq and Afghanistan, military leaders and dissidents.

