The digital revolution is perhaps the most important event of the 21st century, disrupting the status quo of every aspect of our lives as we know it.
Digital technologies can transform how governments interact with their citizens, the private sector, and their international partners.
In the modern world, citizens expect a seamless end-to-end experience and readily accessible services. To achieve these aims, core government digital systems, data-exchange layers, and a nationwide digital identity-management system are essential.
According to well-respected studies, the most important factor empowering such cross-governmental undertaking is the solid commitment of the political leadership to spearhead the necessary whole-of-government approach to public sector modernization.
Therefore, the most significant indicator of the KRG’s seriousness regarding the government’s digital transformation is the leadership demonstrated by Prime Minister Masrour Barzani. The announcement of the government's digital transformation strategy in October 2022 is clear evidence of leadership’s support and commitment.
StrategyGovernments need to deliver hundreds of services to citizens. For modern service delivery, data from multiple entities needs to be aggregated and exchanged, which requires extremely well-coordinated government backend operations and business-processing optimization. Such undertakings are time- and resource-consuming. The modernization of all government services, in any country, requires multiple government cabinets moving according to a cohesive digital transformation strategy, which is why the strategy and prioritization of the digital systems to be implemented are of great importance for governments to establish its core systems.
KRG’s digital transformation strategy focuses on improvements in three broad areas:
Citizens: improvements in services to citizens Government: improvements in KRG capacity Technology: improvements in digital infrastructureTo deliver and measure these improvements, six core strategic activities have been identified as areas for capability and capacity improvements:
Strengthening digital governance Building digital architecture Building human capital Building capacity for user-centered design Building security and data privacy Strengthening procurementThe KRG has prioritized the system’s key criteria for implementation as follows: to be a strategic fit, to have socioeconomic impact, to be likely to succeed, and to enable the multiplier effect.
Systems Implemented by KRG
The Data CenterTo host and serve core government services, the government has built a state-of-the-art data center where the latest T3 standards and technologies power its core systems, databases and networks. PM Masrour Barzani officially inaugurated the facility in September 2022.
The latest hardware and software virtualization technologies allow this T3-compliant data center to achieve high rack density and is thus capable of hosting hundreds of government services securely and efficiently.
Financial Information Management System (KFMS)A financial management information system provides accurate and timely financial information to its users and will support government leaders in making informed decisions on the allocation of financial resources. It is an essential indicator of the Core Government Systems Index (CGSI) of the World Bank’s GovTech Maturity Index (GTMI).
Under the leadership of Prime Minister Masrour Barzani, the Kurdistan Financial Management System (KFMS) was established in July 2020. The project was a collaboration of teams from the Prime Minister’s Office, the Ministry of Finance and Economy’s General Directorate of Public Accounting, the KRG Department of Information Technology (DIT) and local developers.
KFMS will be Kurdistan’s first fully integrated financial management system. This will deliver significant benefits to the government and the people of Kurdistan through enhanced transparency of public finances, driving accountability across the government.
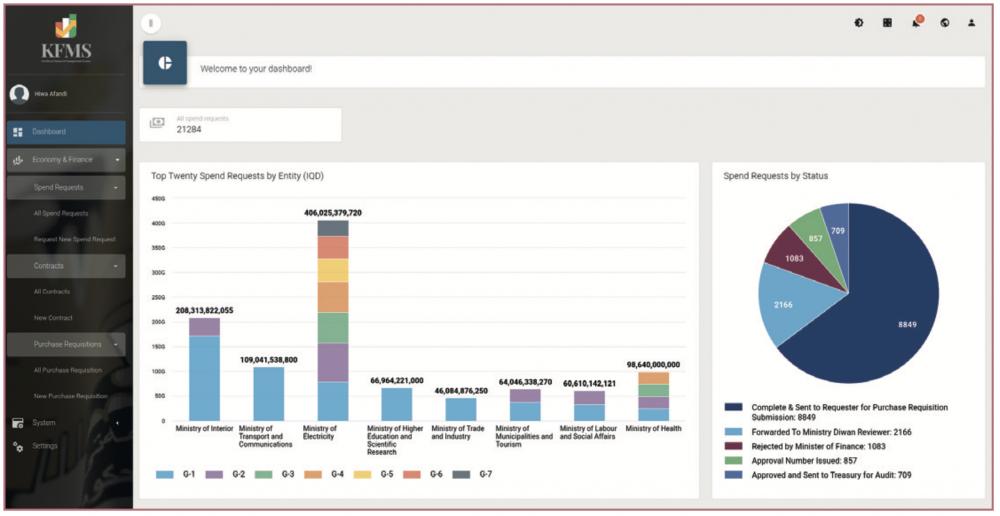
KFMS is also successfully leading the transition from the existing paper-based processes to a digitised version, accelerating processing times, delivering efficiency through automation and improving access to financial data. Recently, paperwork for operational spending from individual ministries’ Accounting Units to the Ministry of Finance and Economy has been eliminated.
Currently, KFMS captures the government’s spending data from the operational expenditure budget. Requests for additional operating expenditure are submitted through KFMS for review and approval or rejection by senior officials and price evaluation experts. As of now, approximately 1,160 Accounting Units across KRG have been onboarded onto KFMS, with thousands of officials trained and equipped to use the system.
In 2023, KFMS will be expanded to incorporate all government expenditures, including capital expenditure and payroll data. Non-oil revenue will also be added to KFMS to give the KRG visibility over the recording and reporting of all of its non-oil revenue data. The digitisation and capture of accurate and timely revenue and expenditure data will allow additional workstreams, such as budgeting and reporting, to be launched.
Population Information System (PIS)Requested directly by PM Masrour Barzani, PIS was developed to address the fundamental difficulties related to the lack of the population census data that is so critical in guiding decision making.
Powered by enterprise-grade database management and biometric identification systems, this digital population registry is the only source of true identity for the new digital systems that the KRG deploys and sits at the core of the data exchange layer of all other services consuming and updating data related to the residing population of the Kurdistan Region of Iraq.
Digital Driver’s License and Vehicle Registration SystemIn partnership with the Germany-based Mühlbauer Group, Kurdistan’s new digital driver’s license and vehicle registration was officially launched in August 2022. To accommodate citizens, this digital service will gradually be made available from 11 locations covering the geographical landscape of the Kurdistan Region of Iraq, offering driver’s licenses and vehicle-registration documents according to international standards and quality.
The new system relies on PIS for identification purposes, and the new driver’s license card is also the 1st official document to assign a digital identity number (UPN) to citizens.
Human Resources Management (HRMS) and Payroll Information Management System (PIMS)HRMS is the centralized information system that manages the payroll information of the KRG’s payees, including but not limited to governmental employees. The system manages a complex payroll management process that breaks down final pay slips for each beneficiary into base salary, allowances, deductions, and many other accounting criteria. HRMS maintains a profile for each beneficiary based on the person’s digital identity number (UPN) retrieved from PIS-Identity. The profile also tracks down the number of benefits and payments a person receives from the KRG, which increases transparency and the identification of ghost employees.
PIMS has already been constructed but its launch is pending the training of thousands of government officials before it officially replaces the old paper-based procedures.
Entry Control System (ECS)ECS is an umbrella project composed of several subsystems that provides for the KRG’s sophisticated systems and tools to control the entry and exit of people to the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. ECS includes the following four subsystems that continuously exchange data between each other: E-Visa System, Entrance/Exit Management System (EEMS), National Stop List (NSL), Guarantor Information Management System (GIMS), Visa Information Management System (VIMS).
Citizen Complaint System (CCS)CCS is a citizen-facing application that allows the people of the Kurdistan Region of Iraq to submit their legal complaints to the government and get feedback digitally in a short period of time. All ministries of the government are being onboarded to CCS to receive complaints digitally. It is an important system, as it is listed as a key indicator in World Bank’s Citizen Engagement Index (CEI) that helps the governments achieve vertical accountability and promote democracy.
Business Entities Administration System (BEAS)BEAS is a central, online digital portal that enables entrepreneurs and businesspeople to register their business with the government in a digital manner and in a much shorter time. It is a central registry for all businesses in Kurdistan, ranging from companies to small shops and startups.
The system generates a Unique Entity Number (UEN) at the end of the registration process that is the single unique identifier of the business across all systems of KRG.
This system sits at the heart of the digitalization of Kurdistan’s economic sector as it provides the foundation for interconnecting business data across multiple sectors and organizations.
It also highly increases efficiency in other related processes such as taxes, since a business’ information can be retrieved from other systems with the UEN acting as a tax identification number (TIN), which saves a considerable amount of time and provides visibility and transparency for those processes.

